Маршрутизатор Cisco C3945-VSEC-CUBE/K9
Почему нет цен?
Уточнить ценуГарантия до 5 лет
Диагностика перед отправкой
С нами выгодно и удобно!
- Поддержка персонального менеджера
- Партнёрские скидки до 70%
- Онлайн-кабинет гарантийного сервиса
Как купить?
Раз, два и все делаРассчитаем стоимость
Присылайте спецификацию для подбора и расчета стоимости оборудования
Привезём и подключим
Подключим и настроим оборудование в вашем офисе или ЦОДе
Характеристики
Отсрочка платежа
В зависимости от суммы поставляемого товара можем предоставить отсрочку платежа на срок от 5 до 90 дней. Условия отсрочки платежа рассматриваются индивидуально. Подробную информацию уточняйте у вашего менеджера.
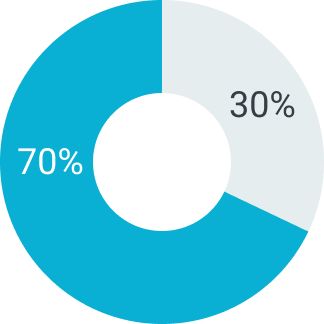
Первый платеж
Второй платеж
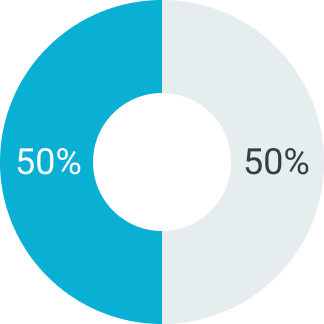
Первый платеж
Второй платеж
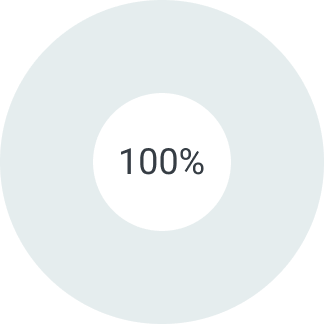
Первый платеж
Второй платеж
Описание
Маршрутизаторы Cisco 3900 Series представляют собой новое поколение устройств, которые являются усовершенствованной версией Cisco 3800 Series. Эти маршрутизаторы предназначены для использования в средних и крупных компаниях, а также в филиалах крупных организаций, обеспечивая высокую производительность, безопасность и гибкость.
Основные характеристики Cisco 3900 Series:
- Консольный порт с поддержкой USB: Устройства оснащены консольным портом, поддерживающим подключение через USB, что упрощает настройку и управление.
- Поддержка управления до 25 точками доступа: При установке дополнительного WLAN контроллера, маршрутизаторы могут управлять до 25 точками доступа, что идеально подходит для расширенной беспроводной сети.
- Универсальный IOS: Cisco 3900 Series использует универсальную прошивку IOS, которая позволяет объединить несколько функций в единую систему, повышая эффективность эксплуатации.
- Высокая пропускная способность: Маршрутизаторы поддерживают пропускную способность до 350 Мбит/с, что обеспечивает быструю обработку и передачу данных.
- Поддержка цифровой обработки сигналов: Для передачи голосовых и видео сообщений используются внутренние разъемы DSP, что обеспечивает высокое качество связи.
- Поддержка модулей ISM: Вместо старых AIM модулей используются новые разъемы под модули ISM, что повышает гибкость и производительность оборудования.
- Совместимость с предыдущими моделями: Наличие слотов EHWIC обеспечивает совместимость с предыдущими моделями маршрутизаторов Cisco 3800 серии, что упрощает модернизацию сети.
- Поддержка PoE (Power over Ethernet): Технология питания через Ethernet снижает расходы на развертывание сети, позволяя питать устройства через тот же кабель, который используется для передачи данных.
- Модульная архитектура: Устройство позволяет добавлять дополнительные модули для увеличения скорости работы и расширения функциональности, благодаря модульной архитектуре.
- Высокоскоростные сетевые соединения: Cisco 3900 поддерживает до 4 сетевых соединений с пропускной способностью до 1 Гбит/с, а также возможность подключения оптических кабелей для высокоскоростной передачи данных.
Маршрутизаторы Cisco 3900 Series предлагают превосходную производительность, масштабируемость и надежность для создания эффективных корпоративных сетей, поддерживающих широкий спектр приложений и служб, включая IP-телефонию, голосовые и видеокоммуникации, а также мультимедийные потоки.
подбор оборудования
до 90 дней












